
 Why is Fukui
Why is Fukui
called the Dinosaur Kingdom?
Let's explore the origin of the Dinosaur Kingdom Fukui together.

1980s: Excavation of dinosaur fossils begins
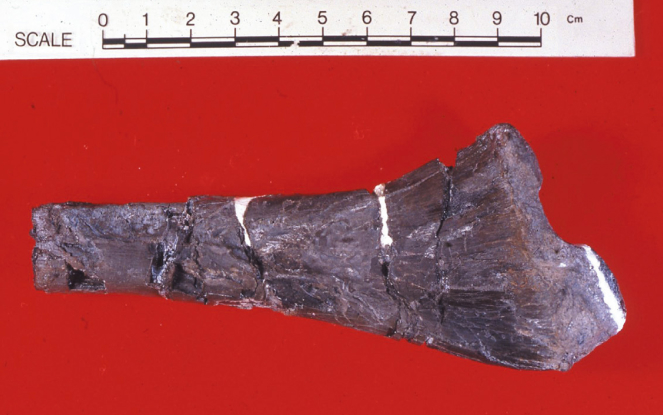

Then an Early Cretaceous crocodile fossil was discovered on a cliff of the Kitadani Formation, Tetori Group in Kitadani-cho, Katsuyama-shi in Fukui. In 1989, this discovery initiated the large-scale excavation of dinosaur fossils, which continues to this day.
This largest dinosaur excavation site in Japan has yielded a series of globally important dinosaur fossils.

1990s: The Japanese dinosaur skeleton was restored for the first time.


2000s: Opening of one of the largest dinosaur museums in the world, the Fukui Prefectural Dinosaur Museum
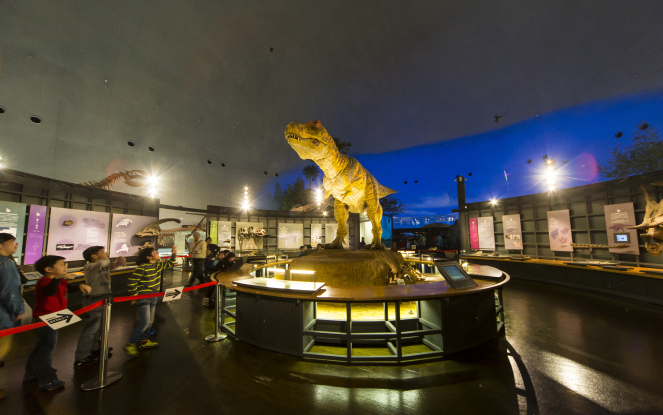

In the same year, Fukuiraptor became the first carnivorous dinosaur to be named in Japan, and with the naming of Fukuisaurus in 2003, the museum captured the attention of dinosaur enthusiasts.

2010s: The Fukui Prefectural Dinosaur Museum continues to grow in popularity and discover new dinosaur species
In addition, the museum continued to discover and name new species of dinosaurs, including Fukuitan in 2010, Koshisaurus in 2015, and Fukuivenator in 2016. In 2017, five types of dinosaur fossils - these three new species, along with Fukuiraptor and Fukuisaurus - and their excavation site were designated as a national natural monument, which is the first case in Japan for dinosaur fossils.
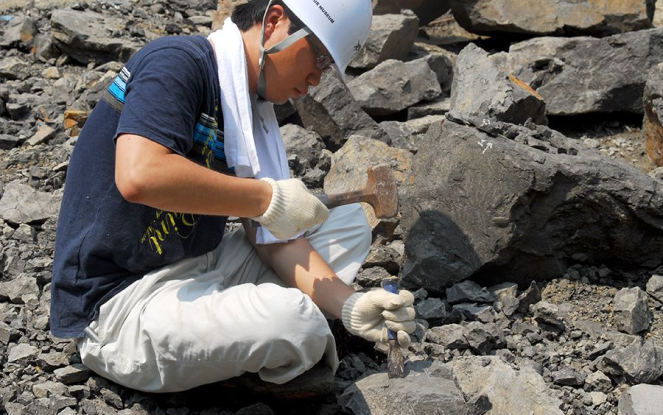

2020s: Dinosaur Kingdom Fukui becomes a household name with more dinosaur research achievements
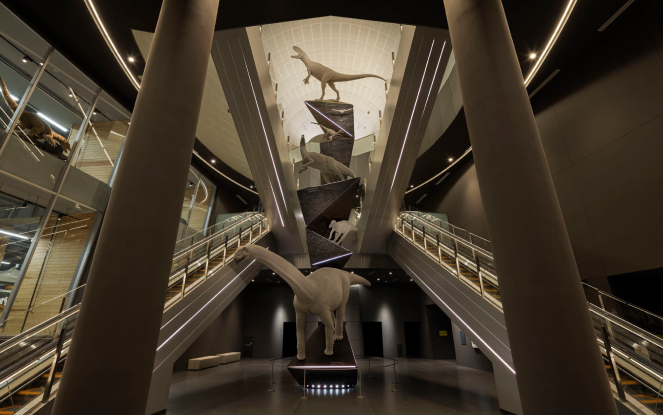

With the announcement of this new species, six of the 11 species of dinosaurs with scientific names in Japan have been discovered in Fukui Prefecture, confirming that "Fukui is associated with dinosaurs" in both name and reality.
We hope you will visit "Dinosaur Kingdom Fukui" and see for yourself.
COLUMN
Why are there so many dinosaur fossils in Fukui?

The Kitadani Formation, Tetori Group, where dinosaur fossils are found, was formed during the age of dinosaurs. At that time, the Japanese archipelago was part of mainland Asia, and a large river flowed through the region. The dinosaurs that lived there could be buried and fossilized in geological layers when, for example, the river flooded.
There are four main reasons for the abundance of dinosaur fossils in Fukui.
The first reason is the discovery of a bonebed - a geological layer containing numerous bone fossils and the like - in the Kitadani Formation. In addition, the stratum is well exposed in cliffs along the river, which makes it easier to collect specimens because the excavation site is easily accessible.
Second, the upper portion of the bonebed was thoroughly excavated by cutting away the entire mountain to fully expose the bone bed.
Third, the excavation has been going on continuously for more than 30 years, mainly led by researchers associated with the Fukui Prefectural Dinosaur Museum.
Fourth, on the basis of excavation surveys, researchers in each field have steadily conducted research by demonstrating their expertise and continuing to publish their findings.
For these reasons, the discovery of numerous dinosaur fossils in Fukui can be attributed to favorable geological conditions and large-scale, continuous excavation, accompanied by the steady research achievements of researchers at the Fukui Prefectural Dinosaur Museum.






